
The steam engine, a marvel of engineering and a cornerstone of the Industrial Revolution, has a rich and fascinating history. From its humble beginnings as a simple pump to its transformation into a powerful engine that drove locomotives, ships, and factories, the steam engine has left an indelible mark on our world. This blog post delves into the captivating history of the steam engine, exploring its origins, evolution, impact, and eventual decline.
Early Experiments with Steam
The concept of harnessing the power of steam dates back to ancient times. In the 1st century AD, Hero of Alexandria, a Greek-Egyptian mathematician and engineer, described a device called the aeolipile. This contraption, also known as Hero’s engine, was a simple steam turbine that spun when the central water container was heated1. While the aeolipile was primarily a novelty, it demonstrated the potential of steam to generate motion2.

Centuries later, inventors began to explore practical applications for steam power. In 1698, Thomas Savery, an English engineer, patented a steam pump that used condensing steam to create a vacuum, which raised water from below, and then used steam pressure to raise it higher3. Savery’s engine, known as the “Miner’s Friend,” was used in mines, pumping stations, and for supplying water to water wheels that powered textile machinery.


The First Practical Steam Engines
In 1712, Thomas Newcomen, another English inventor, developed a more efficient steam engine that used a piston to separate the condensing steam from the water4. Newcomen’s engine, often referred to as an atmospheric engine or a beam engine, was primarily used to pump water out of mines4.


While Newcomen’s engine was a significant improvement over Savery’s pump, it still had limitations in terms of efficiency and power. It was not until the late 18th century that James Watt, a Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer, revolutionized the steam engine with his groundbreaking innovations5.
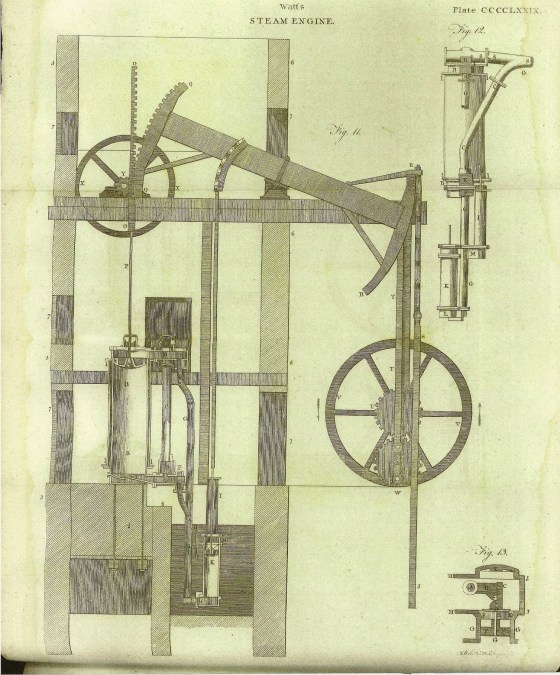
James Watt and the Revolution of Steam
James Watt’s most significant contribution was the separate condenser, which allowed the engine to operate more efficiently by reducing heat loss and minimizing waste6. He also introduced the double-acting engine, which generated power in both the upward and downward strokes of the piston, further increasing efficiency and smoothness7.

Watt’s improvements transformed the steam engine from a crude and inefficient machine into a powerful and versatile tool that could drive machinery in factories, mines, and mills6. His engines were also instrumental in the development of steam locomotives and ships, revolutionizing transportation7.
The Impact of the Steam Engine on the Industrial Revolution
The steam engine played a pivotal role in the Industrial Revolution, a period of unprecedented technological advancement and social change that began in Great Britain in the late 18th century and spread throughout the world8.


Before the widespread adoption of steam power, factories were primarily powered by water, wind, horses, or humans9. These sources had limitations, such as dependence on unpredictable weather conditions or the availability of rivers and streams. The steam engine provided a reliable and consistent source of power that could be used anywhere, regardless of geographical constraints9.
The steam engine’s impact on the Industrial Revolution was far-reaching:
- Factories: Steam engines powered machinery in factories, enabling mass production and increasing the efficiency of manufacturing processes10.
- Mines: Steam engines were used to pump water out of mines, allowing for deeper excavation and increased coal production, which in turn fueled further industrial growth11.
- Transportation: Steam engines powered locomotives and ships, revolutionizing transportation and facilitating trade and commerce10. This led to the expansion of railways and canals, connecting distant regions and enabling the movement of goods and people on an unprecedented scale12.

The steam engine’s impact extended beyond industry and transportation. It also transformed society, leading to urbanization, the growth of cities, and the creation of new jobs13.
Types of Steam Engines and Their Applications

Over time, various types of steam engines were developed, each with its own unique characteristics and applications:
- Stationary engines: These engines were used in factories, mills, and mines to power machinery.
- Marine engines: These engines were used to propel ships and boats.
- Locomotives: These engines were used to power trains.
The development of different types of steam engines led to their use in a wide range of applications, including:

- Agriculture: Steam engines were used to power farm machinery, such as threshing machines and ploughs.
- Construction: Steam engines were used to power cranes and other construction equipment.
- Printing: Steam engines were used to power printing presses.
The Decline of the Steam Engine
Despite its significant contributions, the steam engine eventually began to decline in popularity in the 20th century. This was due to several factors:
- The rise of internal combustion engines: Internal combustion engines, which used liquid petroleum gas or diesel fuel, offered greater power-to-weight ratios and were more efficient for transportation applications3.
- The development of electric motors: Electric motors provided a more efficient and flexible power source for industrial applications3.
- Environmental concerns: Steam engines, particularly those powered by coal, contributed to air pollution12.


By the mid-20th century, steam engines had been largely replaced by internal combustion engines and electric motors in most applications14. However, the steam engine’s legacy lives on, and it remains an important part of our industrial heritage.
Conclusion
The steam engine’s journey through history is a testament to human ingenuity and the power of innovation. From its early beginnings as a simple pump to its transformation into a driving force behind the Industrial Revolution, the steam engine has shaped our world in profound ways. While its reign as the dominant power source may have ended, its impact on technology, industry, and society continues to resonate today.
The Steam Donkey: How a Remarkable Machine Revolutionized the Logging Industry
Embrace the Steampunk Aesthetic with This Stunning 5-Piece Pirate Outfit.
What Is Steampunk?
Works Cited
1. Aeolipile – Wikipedia, accessed December 20, 2024, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aeolipile
2. Smith College Museum of Ancient Inventions: Heron’s Steam Engine, accessed December 20, 2024, https://www.smith.edu/hsc/museum/ancient_inventions/steamengine2.html
3. Steam engine – Wikipedia, accessed December 20, 2024, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steam_engine
4. The Rise of the Steam Engine – National Coal Mining Museum, accessed December 20, 2024, https://www.ncm.org.uk/news/the-rise-of-the-steam-engine/
5. Steam engine | Definition, History, Impact, & Facts – Britannica, accessed December 20, 2024, https://www.britannica.com/technology/steam-engine
6. Matthew Boulton and James Watt: Transformed the Steam Engine – Thomas Earnshaw, accessed December 20, 2024, https://thomas-earnshaw.com/blogs/the-earnshaw-odyssey/matthew-boulton-and-james-watt-transformed-the-steam-engine
7. History of the Watt Steam Engine – Science | HowStuffWorks, accessed December 20, 2024, https://science.howstuffworks.com/innovation/inventions/watt-steam-engine.htm
8. The Steam Engine, the Industrial Revolution and Coal, accessed December 20, 2024, http://history.alberta.ca/energyheritage/coal/early-coal-history-to-1900/the-steam-engine-the-industrial-revolution-and-coal.aspx
9. Watt steam engine | Definition, History, & Facts – Britannica, accessed December 20, 2024, https://www.britannica.com/technology/Watt-steam-engine
10. Steam Power and the Industrial Revolution: How the Steam Engine Changed the World, accessed December 20, 2024, https://thomas-earnshaw.com/blogs/the-earnshaw-odyssey/steam-power-and-the-industrial-revolution-how-the-steam-engine-changed-the-world
11. The Steam Engine | Environment & Society Portal, accessed December 20, 2024, https://www.environmentandsociety.org/mml/steam-engine
12. The Industrial Revolution Was a Steamy Time in History – Petroleum Service Company, accessed December 20, 2024, https://petroleumservicecompany.com/blog/industrial-revolution-steamy-affair/
13. Evolution & History of Steam Locomotives – Strasburg Rail Road Mechanical Services, accessed December 20, 2024, https://mechanical.strasburgrailroad.com/blog/history-steam-locomotive/
14. Running Out of Steam – StoryMaps, accessed December 20, 2024, https://storymaps.com/stories/ec0eefa187a4434ca5eb21d5c88230fd
https://wp.me/pbZSnV-2jC




